File:Map of state religions.svg

לקובץ המקורי (קובץ SVG, הגודל המקורי: 512 × 263 פיקסלים, גודל הקובץ: 1.55 מ"ב)
כיתובים
כיתובים
תקציר[עריכה]
| תיאורMap of state religions.svg |
|
|||
| תאריך יצירה | ||||
| מקור | Derived from BlankMap-World6, compact.svg and British Isles England.svg | |||
| יוצר | Smurfy, Svenskbygderna (talk) | |||
| אישורים והיתרים (שימוש חוזר בקובץ זה) |
אני, בעל זכויות היוצרים על עבודה זו, מפרסם בזאת את העבודה תחת הרישיון הבא:
|
Note[עריכה]
These countries don't have state religions (and must not be erroneously added for this reason):
- Argentina - According to Section 2 of the Constitution of Argentina,"The Federal Government supports the Roman Catholic Apostolic religion." but does not stipulate an official state religion: [1]
- El Salvador - According to Article 26 of the Constitution of El Salvador," The juridical personality of the Catholic Church is recognized. The other churches may obtain recognition of their personality in conformity with the law." but does not stipulate an official state religion: [2] archive copy at the Wayback Machine
- Georgia - According to Article 9 of the of the Constitution of Georgia,"The State shall declare absolute freedom of belief and religion. At the same time, the State shall recognise the outstanding role of the Apostolic Autocephalous Orthodox Church of Georgia in the history of Georgia and its independence from the State." but does not stipulate an official state religion: [3]
- Thailand - There have been protests otherwise, but the constitution does not mention a state religion.[4]
These countries don't provide any special status for a particular religion in their constitutions at all:
- Cyprus - Article 18 of the Constitution of Cyprus:[5] archive copy at the Wayback Machine
- Dominican Republic - Article 45 of the Constitution of the Dominican Republic: [6]
- Haiti - Section 2 of Article 30 of the Constitution of Haiti: [7]
- Moldova - Section 4 of Article 31 of the Constitution of Moldova: [8] archive copy at the Wayback Machine
- Slovakia - Section 1 of Article 1 of the Constitution of Slovakia: [9]
References[עריכה]
- Bhutan[1]
- Mauritania[2]
- Western Sahara (via Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic[3] and Morocco[4], which divide control)
- Morocco[4]
- Tunisia[5]
- Egypt[6]
- Jordan[7]
- Iraq[8]
- Afghanistan[9]
- Pakistan[10]
- Bangladesh[11]
- United Arab Emirates[12]
- Oman[13]
- Yemen[14]
- Maldives[15]
- Iran[16]
- Algeria[17]
- Saudi Arabia[18]
- Somalia[19]
- Malaysia[20]
- Brunei[21]
- Finland[22][23]
- Greece[24]
- Denmark[25]
- Norway[26]
- Costa Rica[27]
- Syria[28][29][30][31]
- Sri Lanka[32]
- Zambia[33]
- ↑ https://www.academia.edu/4109874/THE_INSCRUTABLE_GUARDIAN_OF_THUNDER_AND_SILENCE_The_Dragon_druk_in_Himalayan_Symbology
- ↑ Mauritania. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2018-12-24. Retrieved on 2013-02-14.
- ↑ Toby Shelley. Endgame in the Western Sahara: What Future for Africa's Last Colony?. Zed Books; 2004. ISBN 978-1-84277-341-3. p. 174[dead link].
- ↑ a b Morocco. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2021-01-03. Retrieved on 2013-02-14.
- ↑ Tunisia. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2012-10-14. Retrieved on 2013-02-14.
- ↑ The 2012 Constitution of Egypt, Translated by Nivien Saleh, with Index (Article 2)
- ↑ Jordan. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2016-05-21. Retrieved on 2013-02-14.
- ↑ Iraq. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2020-11-25. Retrieved on 2013-02-14.
- ↑ The Constitution of Afghanistan archive copy at the Wayback Machine (Chapter one, Article two), afghan-web.com
- ↑ Pakistan. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2019-12-19. Retrieved on 2013-02-14.
- ↑ Bangladesh. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2020-06-04. Retrieved on 2018-04-13.
- ↑ United Arab Emirates. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2019-01-04. Retrieved on 2013-02-14.
- ↑ Oman. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2018-12-25. Retrieved on 2013-02-14.
- ↑ Yemen. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2016-08-06. Retrieved on 2013-02-14.
- ↑ Maldives. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2015-09-18. Retrieved on 2013-02-14.
- ↑ Iran - Constitution (Article 12), unibe.ch, "The official religion of Iran is Islam and the Twelver Ja'fari school, ..."
- ↑ Algeria. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2020-08-30. Retrieved on 2013-02-14.
- ↑ The Basic Law of Governance archive copy at the Wayback Machine (Chapter one, Article one), saudiembassy.net, "The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is a sovereign Arab Islamic State. Its religion is Islam. Its constitution is Almighty God's Book, The Holy Qur'an, and the Sunna (Traditions) of the Prophet (PBUH). Arabic is the language of the Kingdom. The City of Riyadh is the capital."
- ↑ Somalia. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2019-09-12. Retrieved on 2013-02-14.
- ↑ Federal Constitution archive copy at the Wayback Machine, agc.gov.my
- ↑ (2007) Brunei Sultan Haji Hassanal Bolkiah Mu'Izzaddin Waddaulah Handbook, Int'l Business Publications, pp. 133 ISBN: 978-1-4330-0444-5. [dead link]
- ↑ Kirkkolaki 1054/1993. Finlex.
- ↑ Laki ortodoksisesta kirkosta 985/2006. Finlex.
- ↑ Greece. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2016-08-25. Retrieved on 2013-02-14.
- ↑ Denmark. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2015-09-18. Retrieved on 2013-02-14.
- ↑ Norway. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2020-05-06. Retrieved on 2013-02-14.
- ↑ Title VI, Article 75 archive copy at the Wayback Machine of The Constitution of Costa Rica, costaricalaw.com.
- ↑ A. R. Kelidar, "Religion and state in Syria", Asian Affairs Vol. 5 No. 1, 1974 ("The new document, however, unlike previous ones and the Constitutions of other Arab States, does not state that Islam is the State religion…")
- ↑ T. Stahnke and R. Blitt, "The Religion-State Relationship and the Right to Freedom of Religion or Belief: A Comparative Textual Analysis of the Constitutions of Predominantly Muslim Countries", Georgetown Journal of International Law, Vol. 36, 2005 ("This practice of declaring Islamic law as a basis for legislation also occurs in countries such as Syria and Sudan, which do not have a declared state religion.")
- ↑ R. J. Mouawad. "Syria and Iraq – Repression: Disappearing Christians of the Middle East". Middle East Quarterly, Winter 2001. ("The Ba'th regime, which came to power in Syria in 1963, has an essentially secular orientation… in conformity with the party's secular ideology, it does not recognize Islam as the official religion of the state.")
- ↑ M. H. Kerr. "Hafiz Asad and the Changing Patterns of Syrian Politics". International Journal, Vol. 28 No. 4, 1973. ("The issue, as on several previous occasions during the 1960s, was the 'godlessness' of the Baath, this time signified in the failure of the constitution to mention Islam as the established religion…")
- ↑ Sri Lanka. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2018-12-24. Retrieved on 2016-11-01.
- ↑ Zambia's Constitution of 1991 with Amendments through 2009. CIA World Factbook.
היסטוריית הקובץ
ניתן ללחוץ על תאריך/שעה כדי לראות את הקובץ כפי שנראה באותו זמן.
| תאריך/שעה | תמונה ממוזערת | ממדים | משתמש | הערה | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| נוכחית | 11:19, 22 ביוני 2022 |  | 263 × 512 (1.55 מ"ב) | أحمد الناصر (שיחה | תרומות) | Reverted to version as of 19:02, 30 March 2022 (UTC) I will Revert it in July |
| 11:16, 22 ביוני 2022 | 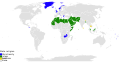 | 263 × 512 (1.55 מ"ב) | أحمد الناصر (שיחה | תרומות) | Tunisia declared its religion not Islam in the upcoming constitution in July. Source: https://www.alhurra.com/tunisia/2022/06/21/%D8%B3%D8%B9%D9%8A%D8%AF-%D9%8A%D8%A4%D9%83%D8%AF-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A5%D8%B3%D9%84%D8%A7%D9%85-%D9%84%D9%8A%D8%B3-%D8%AF%D9%8A%D9%86-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AF%D9%88%D9%84%D8%A9-%D9%81%D9%8A-%D8%AF%D8%B3%D8%AA%D9%88%D8%B1-%D8%AA%D9%88%D9%86%D8%B3-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AC%D8%AF%D9%8A%D8%AF | |
| 19:02, 30 במרץ 2022 |  | 263 × 512 (1.55 מ"ב) | Kwamikagami (שיחה | תרומות) | add names | |
| 08:29, 30 במרץ 2022 |  | 263 × 512 (1.55 מ"ב) | Bayu Fuller (שיחה | תרומות) | add Bahrain, Qatar | |
| 07:36, 30 במרץ 2022 |  | 263 × 512 (1.55 מ"ב) | Bayu Fuller (שיחה | תרומות) | Update Brunei | |
| 23:35, 12 במאי 2020 |  | 263 × 512 (1.53 מ"ב) | Pharexia (שיחה | תרומות) | cleaned up; added crown dependencies, {{https://thediplomat.com/2017/06/samoa-officially-becomes-a-christian-state/ Samoa}}, legend | |
| 20:47, 6 במאי 2020 |  | 776 × 1,760 (1.31 מ"ב) | Paul 012 (שיחה | תרומות) | Thailand does not have an official state religion. | |
| 03:31, 14 בספטמבר 2019 |  | 776 × 1,760 (1.31 מ"ב) | ReiPeixe (שיחה | תרומות) | Both Morocco and the Sahrawi republic recognize Islam as their state religion. (Article 6 of the Sahrawi constitution. Article 2 prescribes that "Islam is the state religion and source of law".) I painted both sides as green and kept the line of control to keep impartiality. | |
| 03:02, 18 ביולי 2019 |  | 900 × 1,600 (827 ק"ב) | BillHPike (שיחה | תרומות) | Reverted to version as of 23:09, 23 April 2019 (UTC) Please provide a reference for the change in Sri Lanka | |
| 10:01, 12 ביוני 2019 | 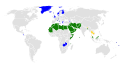 | 900 × 1,600 (866 ק"ב) | AKS471883 (שיחה | תרומות) | ISIS hit Sri Lanka in April 2019 |
אין באפשרותך לדרוס את הקובץ הזה.
שימוש בקובץ
הדפים הבאים משתמשים בקובץ הזה:
שימוש גלובלי בקובץ
אתרי הוויקי השונים הבאים משתמשים בקובץ זה:
- שימוש באתר am.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר ar.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר ast.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר av.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר azb.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר az.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר be-tarask.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר be.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר bg.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר ca.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר cs.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר da.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר de.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר diq.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר el.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר en.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר eo.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר es.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר eu.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר fa.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר fi.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר fr.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר gl.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר he.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר hr.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר hu.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר id.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר ilo.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר inh.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר is.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר it.wikipedia.org
- שימוש באתר ja.wikipedia.org
צפייה בשימושים גלובליים נוספים של קובץ זה.
מטא־נתונים
קובץ זה מכיל מידע נוסף, שכנראה הגיע ממצלמה דיגיטלית או מסורק שבהם הקובץ נוצר או עבר דיגיטציה.
אם הקובץ שונה ממצבו הראשוני, כמה מהנתונים להלן עלולים שלא לשקף באופן מלא את הקובץ הנוכחי.
| רוחב | 100% |
|---|---|
| גובה | 100% |