File:Birkeland-Eyde Plasma Disc.png
Birkeland-Eyde_Plasma_Disc.png (595 × 584 pixels, file size: 161 KB, MIME type: image/png)
Captions
Captions
Summary[edit]
Birkeland-Eyde style plasma disc. Two water-cooled copper tube electrodes are connected to a high voltage alternating current supply (connections and power supply are not shown) to produce a spark gap. Water circulates through the tubes to keep them cool as shown by the arrows. Direct current is applied to the electromagnet.
The arc starts between the electrodes and moves outward forming a semicircle due to the Lorentz force applied by the static magnetic field. Once the arc length becomes too long, a new one forms in the center between the electrodes and the process begins again. The direction the arc moves depends on the polarity. A high voltage alternating current results in a plasma disc, but pulsed DC results in a half disc.
Based on diagrams and description from the book "The Fixation of Atmospheric Nitrogen"[1] and a photo of the electrodes:
Licensing[edit]
| Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse |
| I, the copyright holder of this work, release this work into the public domain. This applies worldwide. In some countries this may not be legally possible; if so: I grant anyone the right to use this work for any purpose, without any conditions, unless such conditions are required by law. |
- ↑ Knox, Joseph (1914) The Fixation of Atmospheric Nitrogen, D. Van Nostrand Company, pp. 45−50
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 01:02, 24 December 2019 | 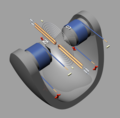 | 595 × 584 (161 KB) | TreeOfKnowledge (talk | contribs) | Reshape the electromagnet to more closely resemble that of a Birkeland-Eyde reactor |
| 12:44, 22 December 2019 |  | 632 × 678 (182 KB) | TreeOfKnowledge (talk | contribs) | Birkeland-Eyde style plasma disc. Two water-cooled copper tube electrodes are connected to a high voltage alternating current supply (connections and power supply are not shown) to produce a spark gap. Water circulates through the tubes to keep them cool as shown by the arrows. Direct current is applied to the electromagnet. The spark starts between the electrodes and moves outward in an arc due to the Lorentz force applied by the static magnetic field. Once the spark length becomes too... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage on Commons
The following page uses this file:
File usage on other wikis
The following other wikis use this file:
- Usage on ar.wikipedia.org
- Usage on en.wikipedia.org
- Usage on uk.wikipedia.org
- Usage on zh.wikipedia.org

