File:Coordination of Cell Polarity during Xenopus Gastrulation A heterogeneous combination of tissues can confer planar cell polarity..png

Original file (2,916 × 4,607 pixels, file size: 4.35 MB, MIME type: image/png)
Captions
Captions
Summary[edit]
| DescriptionCoordination of Cell Polarity during Xenopus Gastrulation A heterogeneous combination of tissues can confer planar cell polarity..png |
Reset zoom All Figures Next Previous Figure 4. A heterogeneous combination of tissues can confer planar cell polarity. (a) The single culture of animal cap expressing a high concentration of Nodal mRNA (125–150 pg: NAC). (b) Combined culture of uninjected animal cap (AC) and NAC. Homogenous combined cultures of NAC (c) and AC (d). The EB3 in the cells in panels a–d respectively, was tracked. (a'–d') Rose diagrams of the EB3 movements in cells a–d. (e) RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) analysis of low concentration of Nodal-mRNA (25–75 pg) injected animal caps. Animal caps into which a relatively high concentration of Nodal mRNA (75 pg: SN-AC) was injected expressed the chordamesoderm and somite marker, Xnot and XmyoDa, papc, and those receiving a relatively low concentration of Nodal mRNA (37.5–50 pg: S-AC) expressed only the somite marker, XmyoD. (f) RT-PCR analysis of high concentration of Nodal-mRNA (150 pg–300 pg: NAC, H-NAC). (g) The angle of the cell body in relation to the border in NAC (150 pg) combined with explants treated with different Nodal levels (0–75 pg of mRNA). Cell alignment perpendicular to the boundary, representing the mediolateral polarity, was observed when the combination was heterogeneous and loss when the combination became more homogeneous (37.5–75 pg). (per: perpendicular, para: parallel, ran: random) (h) The ratio of perpendicularly aligned cells in relation to the border was altered by difference of nodal signaling level. The cells in H-NAC (250 pg) tended to align perpendicular to the border with S-AC (37.5–50 pg). Scale bars, 20 mm (a–d). Each scale of the rose diagrams corresponds to 10% |
| Date | |
| Source | https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0001600 Coordination of Cell Polarity during Xenopus Gastrulation. PLoS ONE 3(2): e1600. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001600 |
| Author | Shindo A, Yamamoto TS, Ueno N |

|
This file, which was originally posted to an external website, has not yet been reviewed by an administrator or reviewer to confirm that the above license is valid. See Category:License review needed for further instructions.
|
Copyright: © 2008 Shindo et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Licensing[edit]
- You are free:
- to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work
- to remix – to adapt the work
- Under the following conditions:
- attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 01:54, 27 April 2024 | 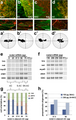 | 2,916 × 4,607 (4.35 MB) | Rasbak (talk | contribs) | {{Information |description= Reset zoom All Figures Next Previous Figure 4. A heterogeneous combination of tissues can confer planar cell polarity. (a) The single culture of animal cap expressing a high concentration of Nodal mRNA (125–150 pg: NAC). (b) Combined culture of uninjected animal cap (AC) and NAC. Homogenous combined cultures of NAC (c) and AC (d). The EB3 in the cells in panels a–d respectively, was tracked. (a'–d') Rose diagrams of the EB3 movements in cells a–d. (e) RT-PCR (reve... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage on Commons
There are no pages that use this file.
Metadata
This file contains additional information such as Exif metadata which may have been added by the digital camera, scanner, or software program used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details such as the timestamp may not fully reflect those of the original file. The timestamp is only as accurate as the clock in the camera, and it may be completely wrong.
| Horizontal resolution | 585 dpc |
|---|---|
| Vertical resolution | 585 dpc |