File:Eta Carinae (1991-10-42).jpg
From Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Size of this preview: 800 × 591 pixels. Other resolutions: 320 × 236 pixels | 640 × 473 pixels | 1,024 × 757 pixels | 1,280 × 946 pixels | 2,560 × 1,892 pixels | 3,249 × 2,401 pixels.
Original file (3,249 × 2,401 pixels, file size: 214 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
File information
Structured data
Captions
Captions
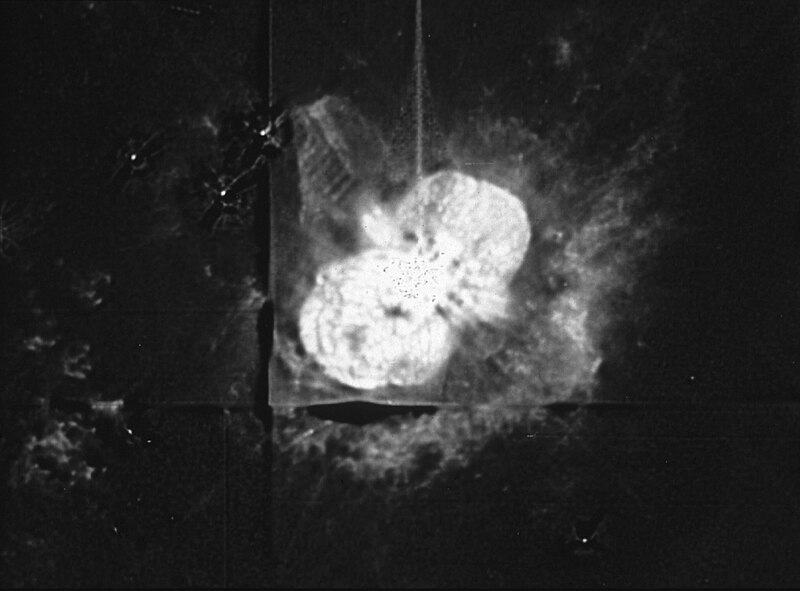
A Hubble Space Telescope observation of the star Eta Carinae, made with the Wide Field and Planetary Camera (WF/PC). An eruptive variable star, Eta Carinae has expelled a large amount of gas into the surrounding interstellar medium.
Summary[edit]
| DescriptionEta Carinae (1991-10-42).jpg |
English: A Hubble Space Telescope observation of the star Eta Carinae, made with the Wide Field and Planetary Camera (WF/PC). An eruptive variable star, Eta Carinae has expelled a large amount of gas into the surrounding interstellar medium. The HST resolves individual clumps as small as only about ten times the size of our Solar System. Because it is clumpy on such small scales, and has such a well defined edge, the nebula is probably a thin and well defined shell of material, rather than a filled volume. Radiation pressure and stellar wind from Eta Carinae have fragmented the shell. Ejecta from the star slams into slower moving gas to create a ridge of emission to the lower right. This ridge is in fact part of a "cap" of material located to the southwest and behind the star. Small knots and filaments trace the locations of other shock fronts within the nebula. A very well collimated jet of material flowing away from Eta Carinae can be seen as two parallel lines pointing to the northeast (upper left) away from the star. These two lines mark the edges of the jet, which appears to be a narrow tube-like structure. The jet terminates in an inverted U-shaped feature, which is the bow shock. A fascinating "ladder-like" structure also appears to be associated with the jet. The "rungs" of the ladder may represent some kind of wave phenomenon in the flow of material away from the star. Seven individual exposures were obtained through a filter which isolates light emitted by ionized nitrogen. The exposures were then combined and processed to partially correct for the aberration caused by the telescope's primary mirror. The field shown is 50 arcseconds across, resolution is 0.2 arcseconds. Not all of the structure in the image is real. The cross centered below and to the left of the star is where the four portions of the image (from four different cameras) were imperfectly patched together. Some of the structure along the left side and bottom of the image is due to imperfections in the image reconstruction techniques. The line and the "Christmas tree" structure extending from the star to the top of the frame and the "salt and pepper" structure in the center of the image are due to overexposure in the center of the nebula. |
| Date | 17 May 1991 (upload date) |
| Source | Eta Carinae |
| Author | Credit:: J. Hester/Caltech & NASA |
| Other versions |
|
Licensing[edit]
| Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse |
| This file is in the public domain because it was created by NASA and ESA. NASA Hubble material (and ESA Hubble material prior to 2009) is copyright-free and may be freely used as in the public domain without fee, on the condition that only NASA, STScI, and/or ESA is credited as the source of the material. This license does not apply if ESA material created after 2008 or source material from other organizations is in use. The material was created for NASA by Space Telescope Science Institute under Contract NAS5-26555, or for ESA by the Hubble European Space Agency Information Centre. Copyright statement at hubblesite.org or 2008 copyright statement at spacetelescope.org. For material created by the European Space Agency on the spacetelescope.org site since 2009, use the {{ESA-Hubble}} tag. |
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 22:35, 30 January 2024 |  | 3,249 × 2,401 (214 KB) | OptimusPrimeBot (talk | contribs) | #Spacemedia - Upload of https://stsci-opo.org/STScI-01EVTB8WJJ0H4CE8DV0V1TA6Z8.jpg via Commons:Spacemedia |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage on Commons
The following page uses this file:
Metadata
This file contains additional information such as Exif metadata which may have been added by the digital camera, scanner, or software program used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details such as the timestamp may not fully reflect those of the original file. The timestamp is only as accurate as the clock in the camera, and it may be completely wrong.
| JPEG file comment | xat.com Image Optimizer |
|---|

