File:HAARP ionogram.gif
Da Wikimedia Commons, l'archivio di file multimediali liberi
Vai alla navigazione
Vai alla ricerca
HAARP_ionogram.gif (720 × 540 pixel, dimensione del file: 58 KB, tipo MIME: image/gif)
Informazioni sul file
Dati strutturati
Didascalie
Didascalie
Aggiungi una brevissima spiegazione di ciò che questo file rappresenta
Dettagli[modifica]
| DescrizioneHAARP ionogram.gif |
English: This ionogram shows a well-formed F-Layer with a peak ionization at around 220 km. There is also a less obvious E-Layer at an altitude of about 110 km. The ionogram clearly shows how the transmitted digisonde signal splits into reflected ordinary and extraordinary waves. The ionogram chart and the parameter FoF2 in the list on the left side of the chart, show that the highest frequency that will be reflected from the ionosphere for vertical incidence (ie., for a radio wave traveling straight up from the ground) is 4.8 MHz. |
| Data | |
| Fonte | http://www.haarp.alaska.edu/haarp/dsonde.html (archived: https://web.archive.org/web/20130404234733/http://www.haarp.alaska.edu/haarp/dsonde.html ) |
| Autore | HAARP |
| Licenza (Riusare questo file) |
http://www.haarp.alaska.edu/haarp/privacy.html (archived: https://web.archive.org/web/20130518024337/http://www.haarp.alaska.edu/haarp/privacy.html ) |
| Altre versioni |
 |
| Posizione del soggetto | 62° 23′ 30″ N, 145° 09′ 00″ W | Posizione di questa e altre immagini su: OpenStreetMap |
|---|
Licenza[modifica]

|
Il detentore del copyright di questo file permette a chiunque di utilizzarlo per qualsiasi scopo, a condizione che il detentore del copyright venga riconosciuto come tale. Sono consentiti la redistribuzione, la modifica, l'uso commerciale ed ogni altro utilizzo. |
|
Attribution |
Cronologia del file
Fare clic su un gruppo data/ora per vedere il file come si presentava nel momento indicato.
| Data/Ora | Miniatura | Dimensioni | Utente | Commento | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| attuale | 17:31, 22 giu 2008 | 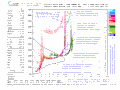 | 720 × 540 (58 KB) | Sebman81 (discussione | contributi) | {{Information |Description={{en|1=This ionogram shows a well-formed F-Layer with a peak ionization at around 220 km. There is also a less obvious E-Layer at an altitude of about 110 km. The ionogram clearly shows how the transmitted digisonde signal split |
Impossibile sovrascrivere questo file.
Utilizzo del file
La seguente pagina usa questo file:
- File:Dsonde.gif (reindirizzamento file)
Metadati
Questo file contiene informazioni aggiuntive, probabilmente aggiunte dalla fotocamera o dallo scanner usati per crearlo o digitalizzarlo. Se il file è stato modificato, alcuni dettagli potrebbero non corrispondere alla realtà.
| Commento del file GIF | Software: Microsoft Office |
|---|
