File:Averages (%) of foods containing appropriate levels of positive nutrients (to achieve adequate intake of any positive nutrient) based on the proposed method in food groups.pdf
Original file (4,964 × 7,020 pixels, file size: 389 KB, MIME type: application/pdf)
Captions
Captions
Summary[edit]
| DescriptionAverages (%) of foods containing appropriate levels of positive nutrients (to achieve adequate intake of any positive nutrient) based on the proposed method in food groups.pdf |
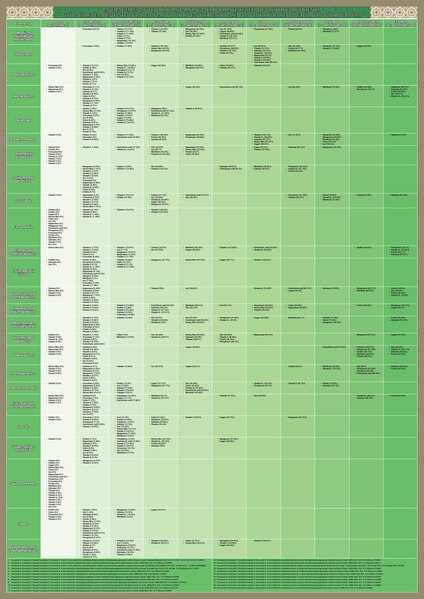
English: About 96.5% of foods contained calcium. On the basis of the proposed method, the average (%) of foods containing appropriate calcium levels in food groups was 11.38%, of which 8.39% was the average of calcium source (good source of calcium) foods, and 2.99% was the average of high-calcium (excellent source of calcium) foods. About 96.5% of foods contained choline. On the basis of the proposed method, the average (%) of foods containing appropriate choline levels in food groups was 21.91%, of which 19.35% was the average of choline source (good source of choline) foods, and 2.56% was the average of high choline (excellent source of choline) foods. |
| Date | |
| Source | Own work |
| Author | SSamadi15 |
Licensing[edit]
- You are free:
- to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work
- to remix – to adapt the work
- Under the following conditions:
- attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- share alike – If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same or compatible license as the original.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 14:21, 2 November 2023 |  | 4,964 × 7,020 (389 KB) | SSamadi15 (talk | contribs) | Uploaded own work with UploadWizard |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage on Commons
There are no pages that use this file.
Metadata
This file contains additional information such as Exif metadata which may have been added by the digital camera, scanner, or software program used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details such as the timestamp may not fully reflect those of the original file. The timestamp is only as accurate as the clock in the camera, and it may be completely wrong.
| Date and time of digitizing | 23:15, 31 October 2023 |
|---|---|
| Date metadata was last modified | 23:15, 31 October 2023 |
| File change date and time | 23:15, 31 October 2023 |
| Software used | Adobe InDesign 17.2 (Windows) |
| Unique ID of original document | xmp.did:b04a1640-05dd-5246-aa20-ed0ce917587a |
| Conversion program | Adobe PDF Library 16.0.7 |
| Encrypted | no |
| Page size | 2383.94 x 3370.39 pts (A0) |
| Version of PDF format | 1.4 |