Software design patterns
Design patterns is a general reusable solution to some commonly occurring problem in software design.
Creational patterns[edit]
Creational patterns deal with object creation mechanisms, trying to create objects in a manner suitable to the situation.
Abstract factory[edit]
The abstract factory pattern provides a way to encapsulate a group of individual factories that have a common theme.
-
gif version
-
svg version
-
png version
-
another png version
Factory method[edit]
the Factory method pattern deals with the problem of creating objects (products) without specifying the exact class of object that will be created.
-
PNG
-
SVG
-
Another PNG
-
Another PNG (in portuguese)
Builder pattern[edit]
The Builder pattern separate the construction of a complex object from its representation so that the same construction process can create different representations
-
svg version
-
png version
Prototype pattern[edit]
Prototype pattern is used when the type of objects to create is determined by a prototypical instance, which is cloned to produce new objects
-
svg version
-
png version
-
another png version
More examples[edit]
- Lazy initialization pattern is the tactic of delaying the creation of an object, the calculation of a value, or some other expensive process until the first time it is needed
- Object pool is a set of initialised objects that are kept ready to use, rather than allocated and destroyed on demand
- Singleton pattern restrict instantiation of a class to one object
Structural pattern[edit]
Structural Design Patterns ease the design by identifying a simple way to realize relationships between entities.
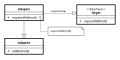
Adapter pattern[edit]
The adapter pattern adapts one interface for a class into one that a client expects
-
Using delegation
-
Using inheritance
Bridge pattern[edit]
The bridge pattern decouple an abstraction from its implementation so that the two can vary independently.
-
gif version
-
png version
-
svg version
-
after (svg)
Composite pattern[edit]
The composite pattern is a tree structure of objects where every object has the same interface.
-
png version
-
svg version
More examples[edit]
- Java Design Patterns Learning Design Patterns
- w:Aggregate pattern: a version of the Composite pattern with methods for aggregation of children
- w:Decorator pattern: add additional functionality to a class at runtime where subclassing would result in an exponential rise of new classes
- w:Extensibility pattern: aka. Framework - hide complex code behind a simple interface
- w:Facade pattern: create a simplified interface of an existing interface to ease usage for common tasks
- w:Flyweight pattern: a high quantity of objects share a common properties object to save space
- w:Proxy pattern: a class functioning as an interface to another thing
- w:Pipes and filters: a chain of processes where the output of each process is the input of the next
- w:Private class data pattern: restrict accessor/mutator access
Behavioral pattern[edit]
behavioral design patterns identify common communication patterns between objects and realize these patterns.
Strategy pattern[edit]
The strategy pattern defines a family of algorithms, encapsulate each one, and make them interchangeable. Strategy lets the algorithm vary independently from clients that use it.
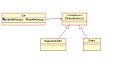
Template method pattern[edit]
The template method pattern describes the program skeleton of a program in an operation, deferring some steps to subclasses.
-
Template Method UML (png)
-
Template Method UML (svg)
-
Template Method UML(2) (svg)
More examples[edit]
- w:Chain of responsibility pattern: Command objects are handled or passed on to other objects by logic-containing processing objects
- w:Command pattern: Command objects encapsulate an action and its parameters
- w:Interpreter pattern: Implement a specialized computer language to rapidly solve a specific set of problems
- w:Iterator pattern: Iterators are used to access the elements of an aggregate object sequentially without exposing its underlying representation
- w:Mediator pattern: Provides a unified interface to a set of interfaces in a subsystem
- w:Memento pattern: Provides the ability to restore an object to its previous state (rollback)
- w:Null Object pattern: designed to act as a default value of an object
- w:Observer pattern: aka Publish/Subscribe or Event Listener. Objects register to observe an event which may be raised by another object
- w:State pattern: A clean way for an object to partially change its type at runtime
- w:Specification pattern: Recombinable Business logic in a boolean fashion
- w:Visitor pattern: A way to separate an algorithm from an object
- w:Single-serving visitor pattern: Optimise the implementation of a visitor that is allocated, used only once, and then deleted
Concurrency pattern[edit]
Concurrency patterns are one of the types of design patterns. Examples of this class of patterns include:
- w:Active Object
- w:Balking pattern
- w:Double checked locking pattern
- w:Guarded suspension
- Leaders/followers pattern
- Monitor Object
- w:Read write lock pattern
- w:Scheduler pattern
- w:Thread pool pattern
- w:Thread-Specific Storage
- w:Reactor pattern
Leaders followers pattern[edit]
Examples of this class of patterns include: